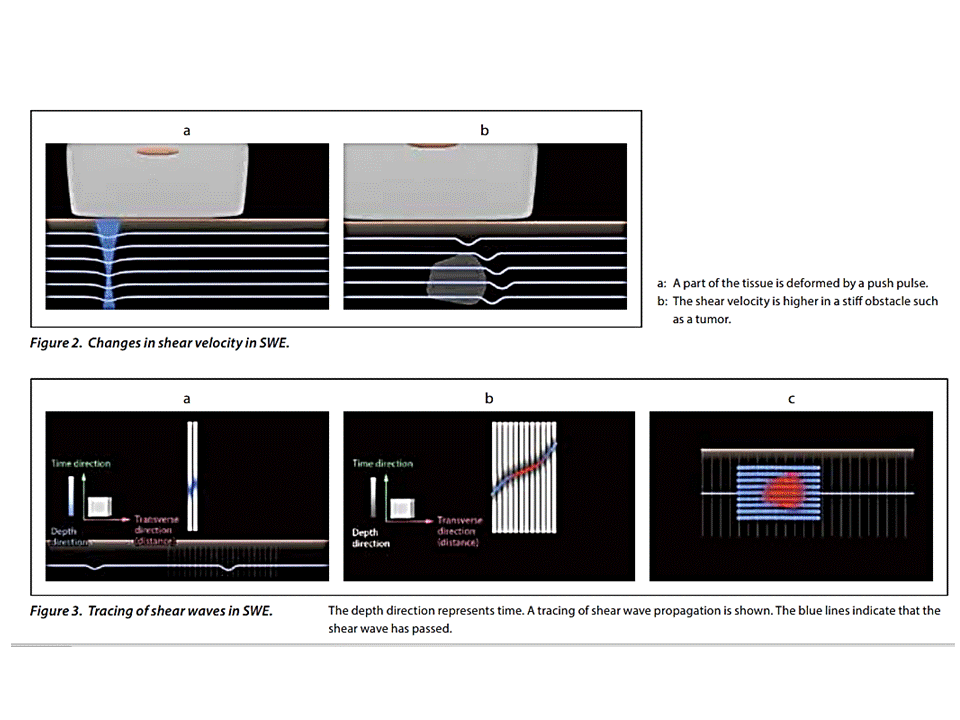
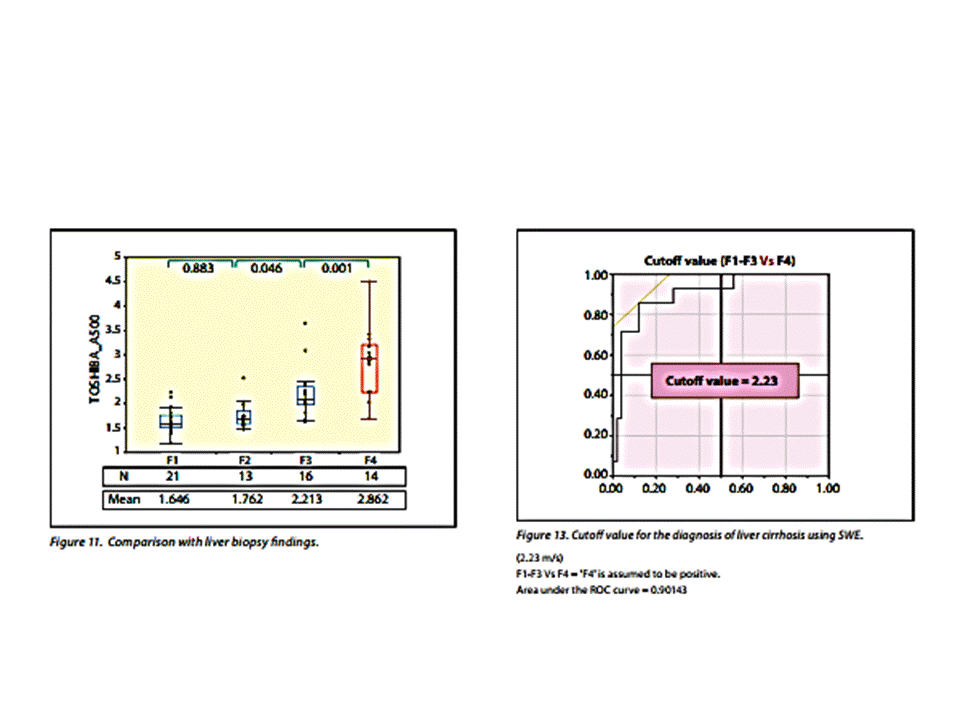
http://www.toshiba-medical.eu/eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2014/09/WP_MOIUS0074EA_Iijima_2014-09.pdf
Tổng số lượt xem trang
Thứ Hai, 22 tháng 2, 2016
SHEAR WAVE ELASTOGRAPHY from APLIO 500 TOSHIBA on LIVER FIBROSIS
DOWNLOAD FULLTEXT
http://www.toshiba-medical.eu/eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2014/09/WP_MOIUS0074EA_Iijima_2014-09.pdf
http://www.toshiba-medical.eu/eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2014/09/WP_MOIUS0074EA_Iijima_2014-09.pdf
Thứ Sáu, 12 tháng 2, 2016
Patient's Platelet Count can Increase the Risk for Hematoma in Liver Biopsy
Image-guided liver biopsy is safe, but not risk-free
By Erik L. Ridley, AuntMinnie staff writer
February 11, 2016 -- While major adverse events from liver biopsy guided by ultrasound or CT are extremely rare, variables such as the patient's platelet count can increase the risk for hematoma from the procedure by as much as fourfold, according to a large retrospective analysis performed at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN.
Thứ Ba, 9 tháng 2, 2016
ULTRASOUND for D V T CAUSE a PULMONARY EMBOLISM
ULTRASOUND for D V T CAUSE a P E
http://www.auntminnie.com/index.aspx?sec=sup&sub=ult&pag=dis&ItemID=113323
Thứ Sáu, 5 tháng 2, 2016
MEDIC ARFI in BREAST TUMORS
CLINICAL
FINDINGS of ARFI in BREAST TUMORS
VO NGUYEN THUC QUYEN, PHAN THANH HAI, MEDIC MEDICAL
CENTER,
HCMC, VIETNAM
INTRODUCTION:
Breast Cancer is currently the top cancer among
women worldwide including Viet nam. Therefore, early detection plays a critical
role in clinical decision of management.
Besides Mammography and MRI, ultrasound has been a useful
modality in detecting breast tumors. Moreover, the combination with Color
Doppler significantly reinforces the B-mode diagnosis. Lately, new ultrasound
technique, elastography is providing more information to increase accuracy. However,
each one uses different method including compressed and non-compressed
technologies. Developing by Siemen, ARFI is a non-compressed elastography,
evaluates tissue stiffness base on replacement caused by acoustic radiation force impulse
(ARFI). In other words, tissue deformed and reformed under a force. The stifferness replaces less
compared with surrounding tissue in same depth. In clinical application, tumors
usually harder than healthy tissue.
AIMS:
To evaluate ARFI qualitative and quantitative assessment
to differentiate benign and malignant breast tumors.
METHODS
and MATERIALS
Patient
and Pathologic diagnosis:
From April to November 2015, we selected 85 breast
lesions classified as category 3-5 according to ACR Breast
Imaging Recording and Data System (BI-RADS). Two radiologists analyzed them in
the following steps before performed biopsy with final diagnosis (FNAC, Core
Biopsy, Excisional Biopsy). All images and biopsy procedures were performed at
Medic Medical Center Ho Chi Minh city. Exclusion criteria include:
·
Non histopathology confirmation
·
Male breast lesions
Imaging
methods:
Using linear probe 9L4 (9MHz) in Siemens Acuson
S2000, we applied respectively 2 modes:
·
VTI (Virtual Touch Quantification): an
gray-scale elasticity map within region of interest (ROI)
·
VTQ: (Virtual Touch Quantification):
quantitatively measure shear-wave speed (m/s) within non-resizable ROI. The ROI
was set in multiple point of the lesion to get the mean measurement.
Step 1: scan B-mode and Color Doppler images,
classified lesion using BI-RADS lexicon (shape, orientation, border,
echotexture, posterior feature)
Step 2:
Acquired Elasticity Score (E.S) in VTI mode then measure Area Ratio (proportion
between VTI lesion area and B-mode area). Base on VTI map, we classified
lesions with 5 elasticity score: Figure
Score
1: totally white
Score
2: mosaic (mix multi-shade of grey and white)
Score
3: black core with white or grey or mix
Score
4: totally or near to complete black
Score
5: totally black with black component out of lesion
Score1-3: low
suspect of malignancy
Score 4-5: high
suspect of malignancy
Step 3: Set ROI in 5 different points of the lesion
then measured Shear-wave Velocity (SWV) in VTQ mode. We calculated mean
velocity for each lesion. The ROI in VTQ mode are fixed with 5 x 5 mm in size.
When acquired velocity reach over 9.10m/s or computer is unable to get the
signal, we have X.XX m/s as value. [1] Figure 2.
Figure 2: Shearwave travels through hard tissue very
fast with > 9.10m/s (X.XX m/s value)
Statistic analysis:
We use SPSS version
16.0 to identified cut-off value and obtain ROC for best value of sensitivity
and specificity. Once we get cut-off value, we use t-student analysis to see
whether benign and malignant populations were statistically different.
RESULT
This study
was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was
obtained from all participants. From April to November 2015, we selected
85 breast lesions including 59 benign (69.4%) and 26 (30.6%) malignant. Lesions
appear to dominantly locate in right breast 52/85 (61.2%), left 33/85 (38.8%).
The mean size 16.26 ±6.56 width and 9.64
±5.01 mm depth
Histopathologic
diagnosis
|
n (%)
|
Malignant: Invasive ductal carcinoma
|
26
(29.4)
|
Benign
|
59
(70.6)
|
Fibroadenoma
|
5
(5.9)
|
Mastitis
|
3
(3.5)
|
Intraductal papilloma
|
2
(2.4)
|
Fibrocystic change
|
46
(55.3)
|
Others
|
3
(3.5)
|
Total
|
85
(100)
|
Table 1: histopathlogic diagnosis of
malignant and benign breast lesions
ARFI analysis
-VTI:
a/
Elasticity Score (E.S)
Malignant
(%)
|
Benign
(%)
|
|
ES
1
|
0
|
0
|
ES
2
|
0
|
52.5
|
ES
3
|
0
|
47.5
|
ES
4
|
23.1
|
0
|
ES
5
|
76.9
|
0
|
Total
|
100
|
100
|
Table 2.1: ES Score frequency of malignant and
benign lesion
As the table 2.1, 26/26 cancer cases has ES 4-5 within
suspicious range.
b/ Area ratio (A.R)
Area Ratio
|
Sensitivity
(%)
|
Specificity (%)
|
1.06
|
100
|
27.2
|
1.13
|
96.2
|
52.5
|
1.20
|
88.5
|
64.4
|
1.34
|
88.5
|
94.9
|
1.40
|
84.6
|
96.6
|
1.44
|
84.6
|
98.3
|
Table 2.2:
As the table 2.2, the AR cut-off point would best at
1.34 with sensitivity 88.5% and specificity 94.9%. Area under ROC curve for
malignancy is 0.933.
-VTQ:
We excluded 8 malignant cases has SWV as X.XX m/s
SWV
|
Sensitivity
(%)
|
Specificity
(%)
|
2.20
|
100
|
69.5
|
2.24
|
94.4
|
72.9
|
2.32
|
88.9
|
79.7
|
2.41
|
83.3
|
83.1
|
2.49
|
77.8
|
88.1
|
Table 2.3:
As the table 2.3, the SWV cut-off point would best
at 2.24 with sensitivity 94.4% and specificity 72.9%. Area under ROC curve for
malignancy is 0.911.
DISCUSSION
The
ability of early detection
ARFI helps in differentiate malignant and benign
lesion. E.S score in VTI mode suggest suspicion are quite accurate in this
study (26/26). The gray-scale map not only distinguish big tumors but also in
small tumors as case demonstrated (Figure 3). It could greatly aid in early detection.
Figure 3: A DCIS 6
x 5 mm mass with BI-RADS 5 in B-mode and ES 5, infiltration is clearly
demonstrated which is not visible on conventional B-mode.
In term of
quantitative evaluation, Area Ratio reinforced E.S. It also shows a better the cancerous
infiltration in surrounding tissue than conventional method. In conventional
ultrasound, only when halo rings, architecture distortion, skin changes suggest
infiltration. However, those present in late stage while we are aiming for
early detection. (Figure 4)
Firgure 4: non-halo
tumors with AR=1.81 is better demonstrated the surrounding invasion
Our cut-off value
Our SWV cut-off
point at 2.24 m/are suitable for clinical practice. Other reference studies were
significantly higher (Yoon
Seok Kim et al: 4.23±1.09 m/sec [2]) as they considered all X.XX value as 9.10m/s.
We excluded all X.XX value since it not actually equals 9.10m/s.
Role
in clinical diagnosis
In clinical application, ARFI increases the accuracy
of B-mode and Color Doppler. It most value in BI-RADS 3-4a lesion which are the
borderline between benignity and malignancy. We recommended grade up from
BI-RADS 3 to 4A if all ARFI features are suspicious. However, here are some
exceptions. Acknowledged that some cancer such as Inflammatory Breast Cancer
(IBC) tends to be softer than normal tissue, reversely, some benign condition
like Mastitis can mask malignancy (figure 5). Our study limited in 85 case and
not included any IBC however caution should be made if specially AR> 1.34.
An interesting study was held by M.Teke et al. which used ARFI to compare Idiopathic
Granulomatous Mastitis with Breast Cancer
. Study shown significantly
different between their SWV (cut-off value 4.08m/s with 80.6% sensitivity,
86.4% specificity). It is important not to miss cancer but still minimalize
invasive option. EFSUMB also recommend this concept but less certain in down
grade. In some situation, we can down grade 4A lesion if the technique done
right, such as circumscribed lesion with suspicious Doppler pattern or
posterior feature. ARFI also helps guiding FNA procedure as we puncture the
hardest points in the lesion on VTI map.
Figure
5: Mastitis lesion in 60 years old patient, BI-RADS 4C E.S 2, AR=1.1 and
VTQ=1.58m/s
Technical recommendation
CONCLUSION
Overall, ARFI is a useful tools for diagnosis and
biopsy guidance breast tumors. The technique is simple since it is non-compressed
and repeatable. It cannot replaced biopsy but reinforced conventional
ultrasound. This is a promising technique helps avoiding invasive diagnosis if
we use it right and well-combined with other features.
REFERENCES:
1/ Wojcinski
S, Brandhorst K, Sadigh G, Hillemanns P, Degenhardt F. Acoustic radiation force
impulse imaging with Virtual TouchTM tissue quantification: mean
shear wave velocity of malignant and benign breast masses. International
Journal of Women’s Health. 2013;5:619-627. doi:10.2147/IJWH.S50953.
2/ Kim
YS, Park JG, Kim BS, Lee CH, Ryu DW. Diagnostic Value of Elastography Using
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging and Strain Ratio for Breast Tumors. Journal
of Breast Cancer. 2014;17(1):76-82. doi:10.4048/jbc.2014.17.1.76.
3/ M.
Teke, M. Gümüş, F. Teke. Combination of elastography and tissue quantification
using the acoustic radiation force impulse technology for differential
diagnosis of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis with Breast Cancer. ECR 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.1594/ecr2015/C-1835
Thứ Hai, 1 tháng 2, 2016
ULTRASOUND ANATOMY INCREASES UNDERSTANDING of LIVING ANATOMY
Abstract
Despite increase in residency programs including ultrasound training, few medical schools have incorporated it into their curricula. The Gross Anatomy course at Mayo Medical School has introduced ultrasound in the curriculum. Cadaver dissection teaches students static anatomical relationships, but ultrasound offers dynamic display of how those relationships can change with movement. Ultrasound curriculum consists of four 1 hour didactic sessions and five 30 minute hands-on modules, covering Carpal tunnel, Heart, Abdominal viscera, and Doppler imaging of blood flow. Each module is guided by a checklist of techniques and structures. Students are graded using ARS system, and ultrasound objectives are incorporated into the final exam. This study aimed to assess effectiveness of ultrasound curriculum in a 7 week anatomy course. Students were asked to complete pre- and post- test surveys that assessed whether ultrasound sessions allowed them to better appreciate living anatomy, learn the basics of operating a portable ultrasound machine, and become more comfortable with medical technology. Pre and post surveys showed that ultrasound helped students appreciate living anatomy, and that they were comfortable with technology. There was an increase in students’ perception of their ability to interpret ultrasound images with a p-value of 0.000026. Ultrasound was a successful addition to the anatomy curriculum.
MEDIC CHUẨN BỊ THAM DỰ AFSUMB 2016
1/ ARFI of TESTIS at MEDIC
CENTER, NGUYEN THIEN HUNG - LE
VAN TAI - PHAN THANH HAI, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER,
HCMC, VIETNAM
3/ CLINICAL APPLICATION of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in BREAST TUMOR at MEDIC CENTER, PHAN THANH HAI PHUONG, VO NGUYEN THUC QUYEN, PHAN THANH HAI
PURPOSE:
Acoustic radiation force
impulse imaging (ARFI) is a new technique for the sonographic quantification of
tissue elasticity. We applied ARFI
elastography to investigate the stiffness of
the normal and pathologic testes.
METHOD and MATERIALS:
20 male volunteers
underwent normal B-mode sonography with ARFI elastometry of both testes using a
Siemens Acuson S2000™ (Siemens Healthcare, Germany) system. 12 cases of
testicular tumor and 03 cases of
hematoma were encountered in our study. Results were statistically
evaluated.
RESULTS:
-
From 40 normal testes of
20 male individuals, mean elastic velocity VTQ= 0.87+/- 0.11m/s [range
0.72-1.12 m/s]
-
From 03 cases of
hematoma, mean elastic velocity VTQ=1.39+/-0.02m/s.
-
From 12 cases of
testicular tumor, mean elastic velocity VTQ= 1.51+/- 0.18 m/s (range
1.26-1.69m/s) with the meaning more stiffness than normal and hematoma testis.
On VTI tumor are harder the parenchyma (black color or blue code)
CONCLUSION:
ARFI elastometry provides the initial values of testicular
stiffness in normal and pathologic status. Further studies with more subjects
may be required to define the normal range of values for normal and pathologic
groups.
2/ARFI for
OBSTRUCTIVE and with UPJO HYDRONEPHROSIS in ALDULT
NGUYEN
THIEN HUNG - TRAN NGAN CHAU- PHAN THANH HAI, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, HCMC,
VIETNAM
ABSTRACT:
We applied ARFI technique from
Siemens S2000 to evaluate whether fibrotic process existing in adult
hydronephrosis.
Using 1-4 MHz convex probe we
calculated in 3 positions of hydronephotic kidney due to obstruction
[stone, outside compression] (n=33 cases), due to ureteropelvic junction
obstruction [UPJO] (n=30 cases]. We had a control group of normal kidney (n=36
cases). Mean value of ARFI velocity of obstruction hydronephrosis (due to
stone) was 2.73+/-0.39m/s and of UPJO hydronephrosis was 1.66+/-0.16m/s while
in control group was 1.6+/-0.2m/s. There were stastistic differences of 2 stone
and UPJO hydronephrosis groups (p < 0.0001), with stone hydronephrosis and
control (p < 0.0001). But no statistic difference exists in UPJO
hydronephrosis and control group.
3/ CLINICAL APPLICATION of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in BREAST TUMOR at MEDIC CENTER, PHAN THANH HAI PHUONG, VO NGUYEN THUC QUYEN, PHAN THANH HAI
INTRODUCTION
Early detection of Breast Cancer plays a critical
role in decision making. Besides mammography and MRI, ultrasound has been a
useful modality in detecting breast tumors. Moreover, the combination with
Color Mode significantly reinforces the B-mode diagnosis. Lately, new
ultrasound technique, elastography is providing extra information to increase
accuracy. However, each one uses different method including compressed and
non-compressed technologies. Developing by Siemens, ARFI is a non-compressed
elastography, evaluates tissue stiffness base on replacement caused by acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI).
AIMS:
To evaluate ARFI qualitative and quantitative
assessment to differentiate benign and malignant breast tumors.
METHODS
and MATERIALS
From April to November 2015, we selected
85 breast lesions classified as category 3-5 according to ACR Breast
Imaging Recording and Data System (BI-RADS). Two radiologists analyzed them in
ARFI features : Elasticity Score (E.S) which on scales 1-5 (Score 1-3: low
suspicion, Score 4-5: high suspect of malignancy), then measure Area Ratio (proportion
between VTI lesion area and B-mode area) and set ROI in 5 different points of
the lesion then measured Shear-wave Velocity (SWV). Biopsy were
required for final diagnosis (FNAC, Core Biopsy, Excisional Biopsy). Exclusion
criteria include: Non histopathology confirmation or Male breast lesion.
RESULT
85 selected breast lesions includes 59 benign
(69.4%) and 26 (30.6%) malignant. Lesions appear to dominantly locate in right
breast 52/85 (61.2%), left 33/85 (38.8%). The mean size is 16.26 ±6.56 transversely
and perpendicularly 9.64 ±5.01 mm. In ES assessment, 26/26 cancer cases were
within suspicious range (
ES4-5). The AR cut-off point would best at 1.34
with sensitivity 88.5% and specificity 94.9% (area under ROC curve for
malignancy is 0.933). After excluded 8 malignant cases has SWV as X.XX m/s, the
best SWV cut-off point is at 2.24 with sensitivity 94.4% and specificity 72.9%
(area under ROC curve for malignancy is 0.911).
CONCLUSION
Overall, ARFI is a useful tools for diagnosis and decision
of biopsy breast tumors. The technique is simple since it is non-compressed and
repeatable. It cannot replaced biopsy but reinforced the Conventional
ultrasound findings. This is a promising
technique helps avoiding invasive diagnosis if we use it right and
well-combined with other features.
4/ Ultrasound findings
of rib fractures in undetected cases by chest x-rays
Le Thanh Liem MD, Phan Thanh Hai MD
Medic Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Abstract:
OBJECTIVE:
METHODS:
RESULTS:
CONCLUSIONS:
Le Thanh Liem MD, Phan Thanh Hai MD
Medic Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Abstract:
OBJECTIVE:
To accumulate
experiences of detection of costal cartilage and rib fractures which are
negative on X-ray films of chest trauma patients.
METHODS:
A total of 112
patients at the Medic Medical Center from 2008 to
2015, suffering from chest trauma, detected costal cartilage or rib
fractures on chest ultrasound with a 7.5 MHz linear transducer of ultrasound.
All patients were examined later by chest X-ray. Statistical analysis was done
to outline the ultrasound findings of these rib fractures.
RESULTS:
In 112 patients
showed costal cartilage and anterior rib
lesions, only 10 patients (9%) showed of rib fracture on chest X-ray film,
whereas 102 other patients (91.0%) had no evidence of rib lesions on chest
X-ray film. Fracture of the rib with a disruption of continuity of bony cortex,
mostly located near the costo-chondral junction. Rib fracture cases that the
displacement is minimal, usually detected by longitudinal plane based on accompanied
by the soft tissue edema or hematoma around the fracture site. Costal cartilage
fractures were in five patients (4,5%). Costal cartilage fracture appeared as
disruption of cortex, small echogenic lines in cartilage, and bruised cartilage.
In addition to detecting rib fractures, ultrasound helps evaluating the stage
of disease based on the presence of hematoma, cartilage callus or bone callus.
Some patients may not specify the position localized pain or may not remember
history of trauma until there is evidence of ultrasound to confirm the
diagnosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Ultrasonography is
a useful imaging modalities in disclosing the rib fractures which were negative
on chest X-ray film in chest trauma.
Although no
significant change in treatment, but the detection of rib fractures is very
helpful in explaining the cause of pain, reducing the anxiety of patients and
avoid other unnecessary diagnostic procedures.
Đăng ký:
Bài đăng
(
Atom
)