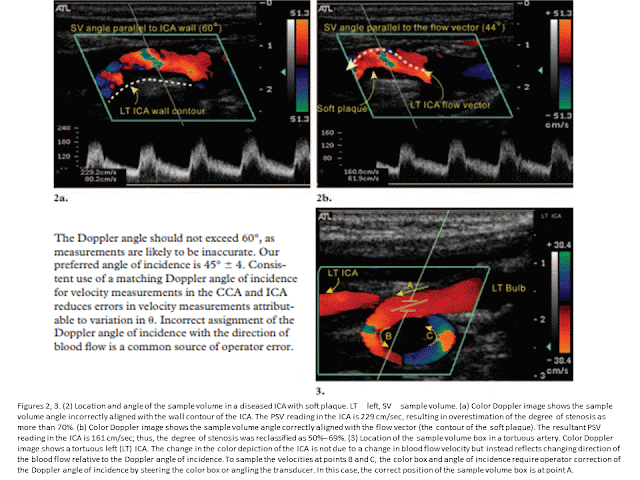
https://www.e-ultrasonography.org/upload/usg-16054.pdf
Doppler ultrasonography of the lower extremity arteries is a valuable technique, although it is
less frequently indicated for peripheral arterial disease than for deep vein thrombosis or varicose
veins. Ultrasonography can diagnose stenosis through the direct visualization of plaques and
through the analysis of the Doppler waveforms in stenotic and poststenotic arteries. To perform
Doppler ultrasonography of the lower extremity arteries, the operator should be familiar with the
arterial anatomy of the lower extremities, basic scanning techniques, and the parameters used in
color and pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasonography.
Doppler
US is the only noninvasive technique that does not require contrast enhancement, preparation of the
patient before the study, or radiation exposure [1,2]. Doppler US is a good method for screening and
follow-up, as well as for the definitive diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease [3-7]. Color Doppler US
can easily identify arteries by finding round objects with regular pulsation and can be used to detect
stenotic or occluded segments [4,8]. Pulsed-wave Doppler US can show the exact flow velocity of
each arterial segment and determine the degree of severity of the stenosis based on an analysis of
the pulsed-wave Doppler spectral waveform [9].
Knowledge of the ultrasonographic anatomy of the lower extremity arteries and the corresponding
anatomical landmarks is essential for performing Doppler US. In this article, we review the basic
scanning techniques of color and pulsed-wave Doppler US for the lower extremity arteries and the
spectral analysis of normal and stenotic arteries on pulsed-wave Doppler US.






Conclusion
Doppler US has been found to distinguish between stenosis with a
diameter reduction greater than or less than 50% (corresponding
to an area reduction of 70%) with a sensitivity of 77%-82% and
a specificity of 92%-98% [18,20-24]. Complete scanning of both
lower extremities may require up to 2 hours depending on the
operator’s experience [18]. However, if the operator is familiar with
the US anatomy of the lower extremity arteries and understands
the parameters and Doppler waveforms of Doppler US, accurate
diagnostic results can be produced with less scanning time.