By Kate Madden Yee, AuntMinnie.com staff writer
June 15, 2018 -- Using intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), researchers from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) have found a link between sensitivity to an allergen in red meat and plaque buildup in the heart's arteries, according to a study published online June 14 in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.
Only recently have scientists identified the main allergen in red meat, called galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose, or alpha-Gal, wrote a team led by Dr. Coleen McNamara from the University of Virginia Health System. It's also been discovered that the lone star tick, found predominately in the southeastern U.S., sensitizes people to this allergen when it bites them, boosting the incidence of meat allergies in this area.
Researchers have suspected for some time that allergens can trigger immunological changes that may be associated with plaque buildup and artery blockages. In their study, McNamara and colleagues showed that a type of antibody (immunoglobulin) specific to the alpha-Gal allergen was associated with higher levels of arterial plaque.
The investigators analyzed blood samples from 118 adults and found antibodies to alpha-Gal in 26%. Next, they used intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) to analyze the quantity of plaque in the blood samples. The amount was 30% higher in the alpha-Gal-sensitized patients than in the nonsensitized patients.
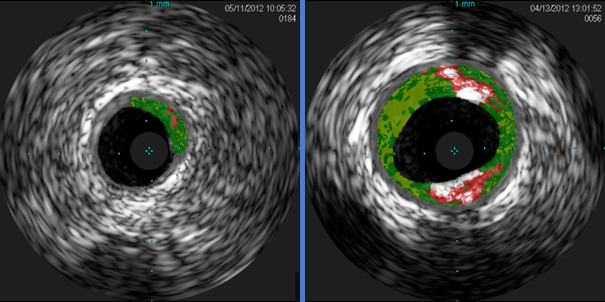
Cross-sectional IVUS images of coronary arteries. Plaque buildup (colored areas) in an artery from a patient who lacks sensitivity to the red meat allergen (left) is much lower than plaque levels in an artery from a patient with sensitivity to the allergen (right). Images courtesy of Dr. Angela Taylor of the University of Virginia Health System.
"This novel finding from a small group of subjects from Virginia raises the intriguing possibility that allergy to red meat may be an underrecognized factor in heart disease," McNamara said in a statement released by the NIH. "These preliminary findings underscore the need for further clinical studies in larger populations from diverse geographic regions and additional laboratory work."
Không có nhận xét nào :
Đăng nhận xét