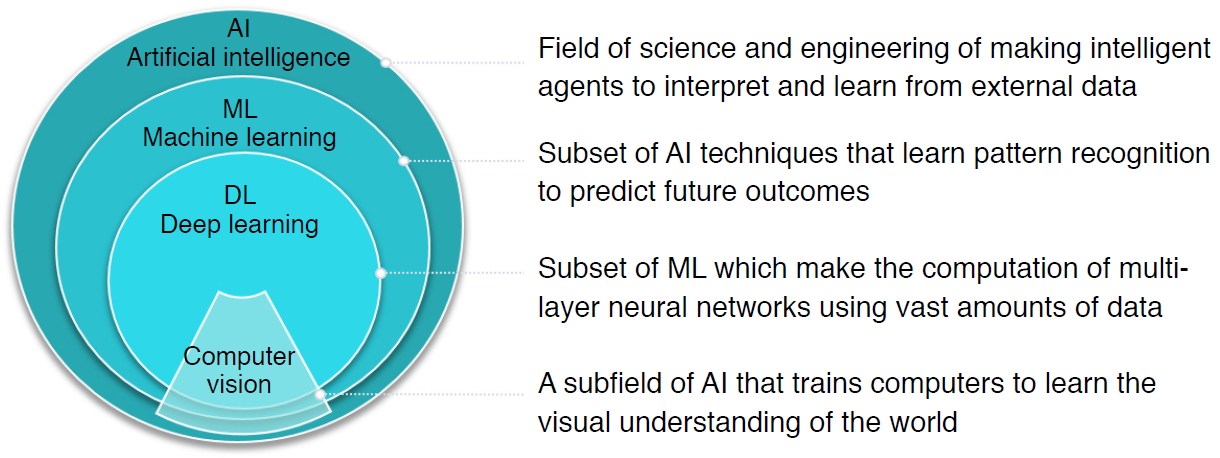
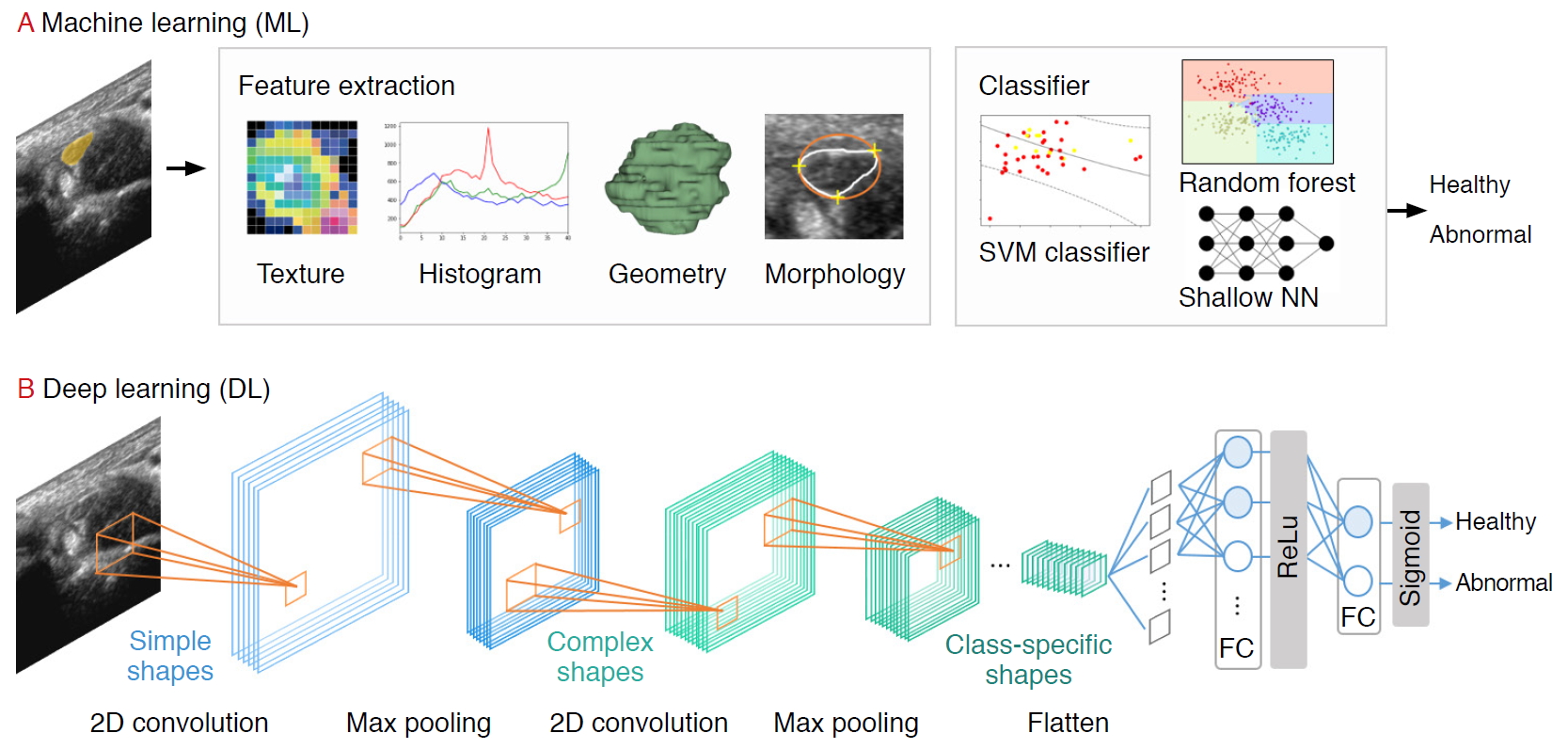
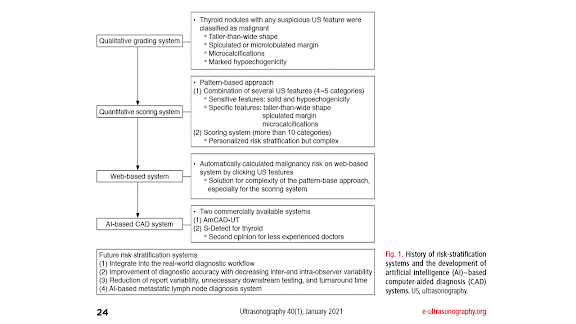
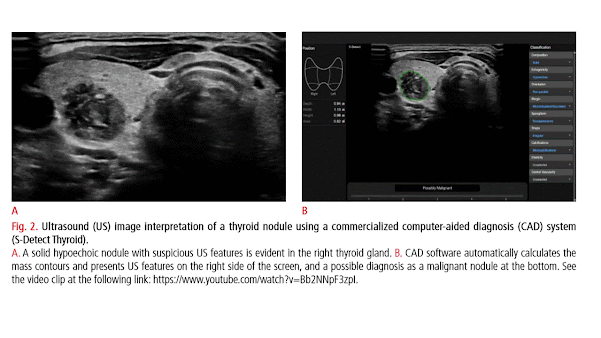
AI in Musculoskeletal US Imaging
 | Fig. 3.Schematic of artificial intelligence (AI)-based machine learning and deep learning applications in musculoskeletal ultrasound imaging of AI-based diagnosis and classification and AI-based automated image segmentation.SVM, support vector machine; KNN, k-Nearest Neighbor; ROI, region of interest. |

Automatic Diagnosis and Detection in Musculoskeletal US
Muscle Disorders
 | Fig. 4.Deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based fiber orientation.A. A representation of DCNN predictions for fiber orientation is given. A fiber orientation heatmap is shown in the top image, and a line trace representation overlaid on the ultrasound image is shown in the bottom image. CNN, convolutional neural network. B. The temporal variation in fiber orientation traces of maximum voluntary contraction (starting at 0 second and ending at 2.2 seconds) is given. Reprinted from Cunningham et al. J Imaging 2018;4:29, according to the Creative Commons license. |

Diagnosis of Hip Dysplasia

Automatic Regression and Classification of Musculoskeletal US
Synovitis Assessment
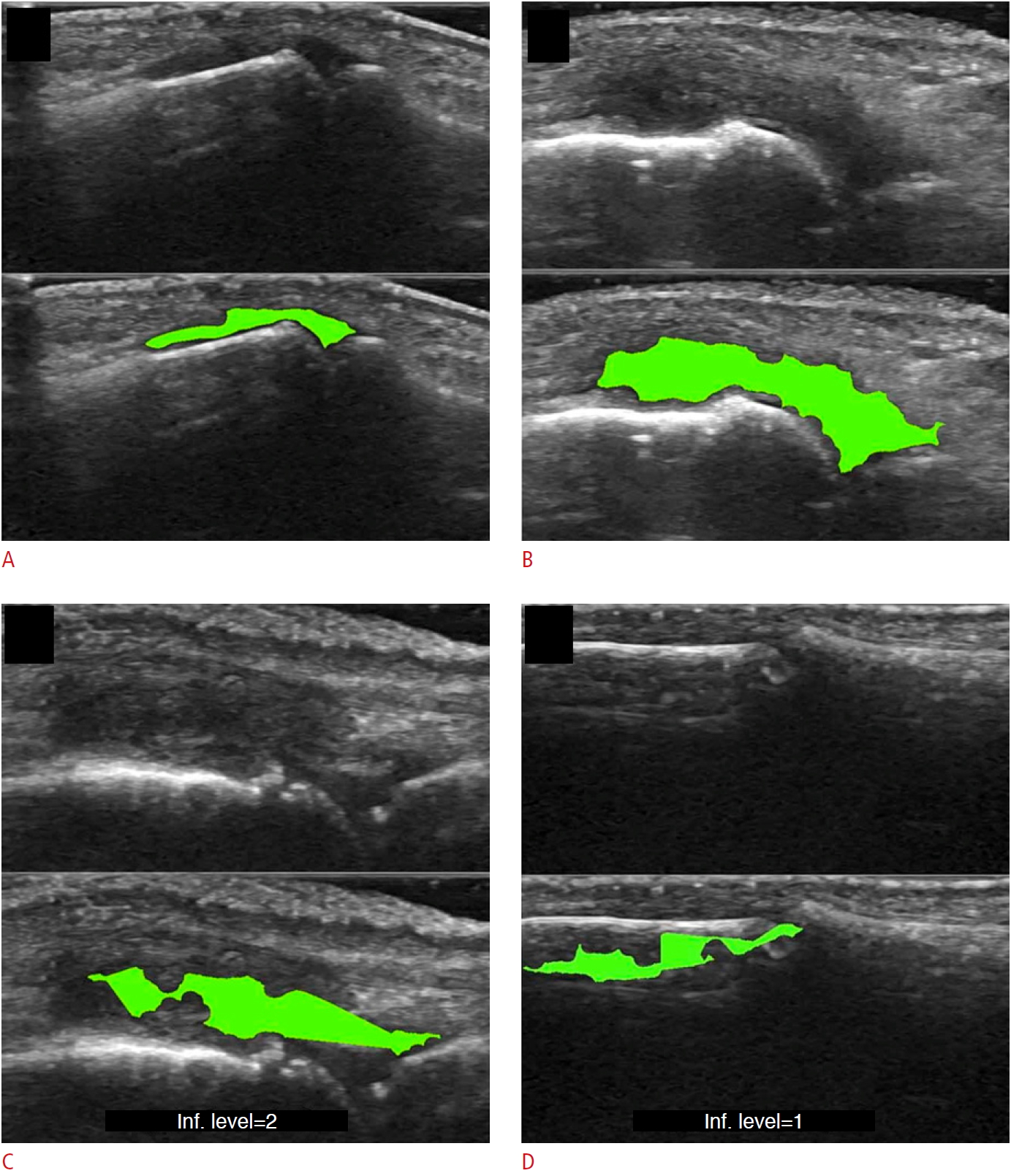 | Fig. 5.Example of synovitis area detection with a machine learning-based pipeline, as suggested by Mielnik et al. [12].A-D. The detection of synovitis in the proximal interphalangeal joint (A), detection of synovitis in the metacarpophalangeal joint (B), example of underestimated region of synovitis (C), example of error in synovial hypertrophy detection (D) are shown. Reprinted from Mielnik et al. Ultrasound Med Biol 2018;44:489-494, Copyright (2020), with permission from Elsevier [12]. |

Spine Level Analysis and Identification
 | Fig. 6.Image identification for lumbar ultrasound image.The pipeline proposed by Yu et al. [11] consists of a feature extraction method to extract important anatomic features and midline detection and classification stage for interspinous region identification. SVM, support vector machine. Reprinted from Yu et al. Ultrasound Med Biol 2015;41:2677-2689, Copyright (2020), with permission from Elsevier [11]. |

Automated US Image Segmentation Techniques
Nerve Localization and Segmentation
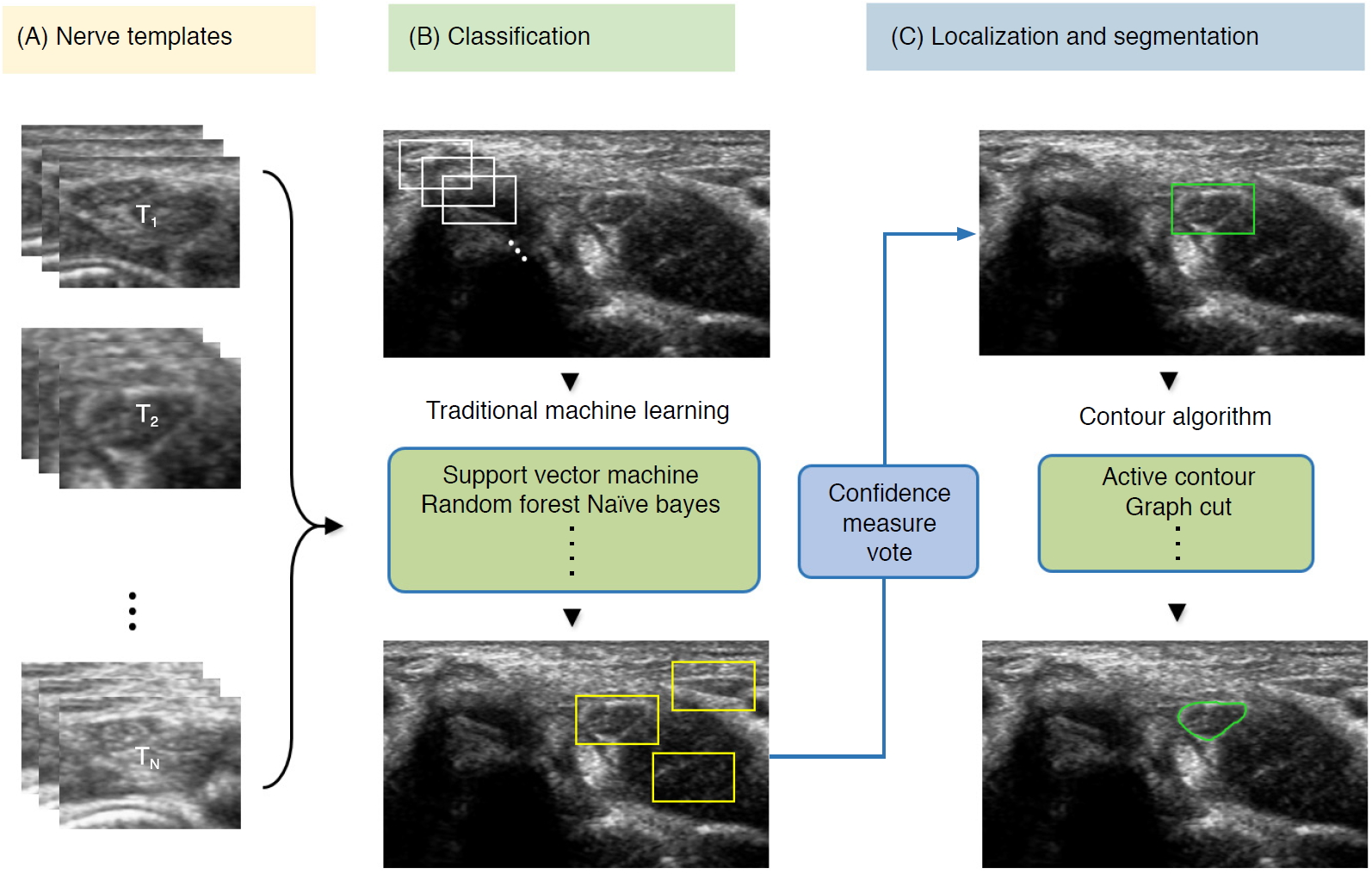 | Fig. 7.Conventional machine learning-based segmentation scheme of nerve ultrasonography.Sliding window template-based classification is applied to generate candidate regions of interest. The nerve region is localized based on a confidence measure vote, and segmentation is applied to obtain nerve boundaries. |
Cartilage Segmentation
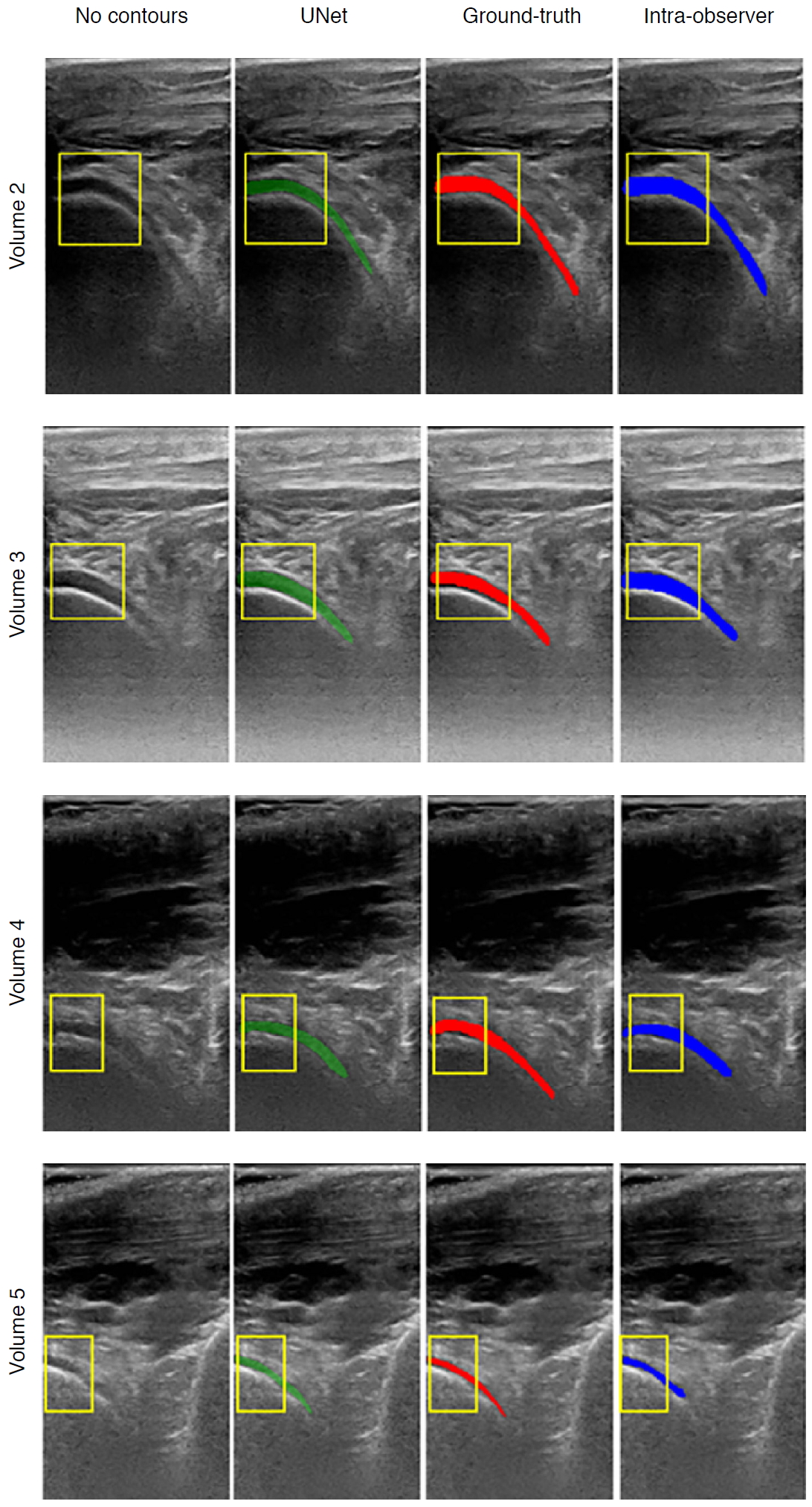 | Fig. 8.Examples of cartilage segmentation based on a U-Net architecture [69].The first column shows examples of images and image regions (yellow box) selected. For each US image in the figure, the segmentations produced by the U-Net (green), by the expert during the ground-truth creation (red), and the intraobserver test (blue) are shown. Reprinted from Antico et al. Ultrasound Med Biol 2020;46:422-435, Copyright (2020), with permission from Elsevier [69]. |

Challenges and Future Perspectives of AI-Based Musculoskeletal US

Conclusion