Tích mỡ trong gan có thể do lạm dụng rượu, một số thuốc men, viêm gan siêu vi, bệnh gan tự miễn, bệnh gan biến dưỡng hoặc di truyền. Loại được tất cả các nguyên nhân này có thể phát hiện gan thấm mỡ không do rượu [NAFL]. Gan thấm mỡ không do rượu có nguy cơ chai gan, với cảnh báo trở thành dịch trong thập niên tới.
(MRI, là một công cụ đánh giá gan thấm mỡ tuyệt vời, nhưng không có khả năng sàng lọc nhanh, chi phí thấp như siêu âm).
Siêu âm B-mode có khả năng phát hiện sớm gan thấm mỡ bằng định tính và các kỹ thuật định lượng, [ bao gồm CAP của FibroScan], góp phần ngăn chặn diễn tiến gan xơ hóa và chai gan.
ĐỊNH TÍNH:
HÌNH ẢNH SIÊU ÂM
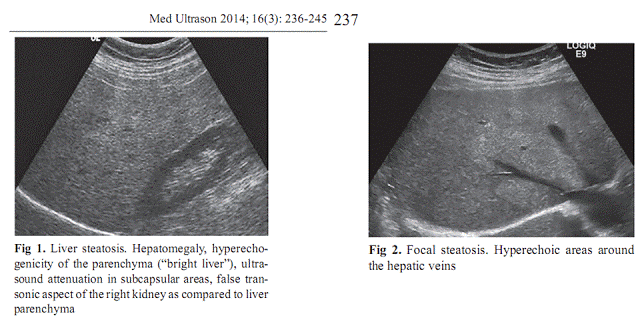
Gan thấm mỡ lan tỏa sinh nhiều echo trên siêu âm B-mode. Các dấu hiệu siêu âm gồm: tăng echo chủ mô gan, vách mạch máu mờ, tăng giảm âm và khó thấy các phần sâu và sát cơ hoành, và gan lớn.
Có 3 mức độ:
+nhẹ, tăng echo nhẹ lan tỏa, còn thấy cơ hoành và vách mạch máu trong gan;
+trung bình, tăng echo trung bình và mờ cơ hoành và vách mạch máu;
+nặng, tăng echo rõ ràng, xuyên thấu kém ở các phân thùy sau gan phải và kém hay không còn thấy vách mạch máu và cơ hoành.
Gan thấm mỡ khu trú là mỡ khu trú trong gan có echo, có thể có dạng khối nhưng thường có đường viền dạng bản đồ, và không làm dời chỗ mạch máu đi qua.
Gan thấm mỡ không hoàn toàn thường là những vùng echo poor quanh tĩnh mạch cửa, thùy đuôi và quanh hố túi mật, đôi khi cần CT xác định lại.
Siêu âm thường không nhạy đối với gan thấm mỡ hạt nhỏ.
Khó phân biệt về siêu âm giữa gan thấm mỡ và xơ gan phản ánh các tiêu chuẩn siêu âm bị trùng lấp và cùng có các tiến trình trên cùng bệnh nhân.
VẤN ĐỀ:
1. Gan thấm mỡ độ nhẹ thường bị bỏ sót.
2. Viêm gan mạn cũng có giảm âm phần sâu.
3. Không phân biệt được bằng siêu âm các nguyên nhân của gan thấm mỡ.
4. Không phân biệt được bằng siêu âm gan thấm mỡ và các loại viêm gan khi có tăng men gan.
Với 101 ca (72 nữ, 55 nam) có làm histogram cường độ siêu âm gan và thận.
• - Tiêu chuẩn chẩn đoán siêu âm :
- gan to (gan trái lớn hơn 10cm qua mặt cắt dọc qua
động mạch chủ bụng, gan phải lớn hơn 15cm qua mặt cắt gian sườn ở bình diện
thận phải).
- mờ vách tĩnh mạch cửa, chỉ chọn các vách giảm echo nhánh xa (gan thấm
mỡ độ nhẹ) và giảm echo vách các nhánh chính (độ vừa).
Kết quả=
1/ Thành phần bệnh nhân
gan thấm mỡ: béo phì (25,74%), tiểu đường (18,81%), rượu (06,93%),
thuốc corticoid và tương tự (0,99%), ăn chay (02,97%)
2/ Đa số gan thấm mỡ độ
nhẹ (76,24%) còn lại độ vừa (19,8%).
3/ Đa số đều tăng triglycerides TG
(59,40% và 66,39%) và có tăng cholesterol CL (66,33% và 72,27%)
Một
số có tăng men gan (gấp 3 trị số bình thường) (41,79%)
Một
số dương tính giả (22/101 và 4/67)
5/ Bình quân độ chênh
lệch histogram cường độ siêu âm gan thận số ca gan thấm mỡ là 730/101 = 7,22.
Kết luận:
1/ Siêu âm chẩn đoán gan thấm mỡ đối chiếu với kết quả sinh hóa có
độ chính xác là 78,21%.
2/ Đa số nguyên nhân gan thấm mỡ của 2 lô nghiên cứu là béo phì và
tiểu đường. Nhưng khó xác định được nguyên nhân vì có nhiều yếu tố ảnh hưởng
cùng lúc (nội tiết, dinh dưỡng, rượu, viêm nhiễm…).
3/ 41,79% có tăng men gan kèm theo tăng TG và CL gợi ý quá trình
gan thấm mỡ diễn biến đã lâu, và cần thiết phân biệt với viêm gan do nhiều
nguyên nhân khác nhau (viêm gan mỡ, steatohepatitis).
ĐỊNH LƯỢNG:
Histogram cường độ siêu âm gan và thận và chỉ số thấm mỡ gan thận [SHRI]
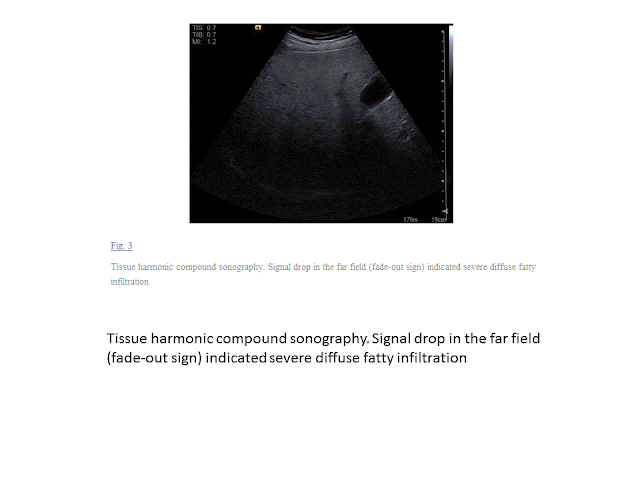
TISSUE HARMONIC COMPOUND SONOGRAPHY
ACOUSTIC STRUCTURE QUANTIFICATION [ASQ]LIVER FAT and FIBROSIS
NHÌN LẠI GAN THẤM MỠ
ARFI ĐÁNH GIÁ ĐỘ CỨNG GAN Ở BỆNH NHÂN TIỂU ĐƯƠNG TYPE 2
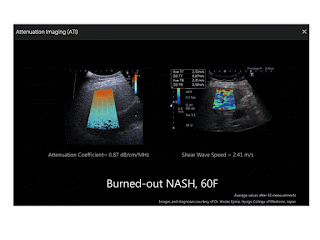
GAN MỠ: ĐÁNH GIÁ CỦA SIÊU ÂM ĐÀN HỒI
TẠO HÌNH ĐÀN HỒI SÓNG BIẾN DẠNG PHÂN TÁN [SWE DISPERSION]
UNUSUAL NODULAR FATTY INFILTRATION of the LIVER